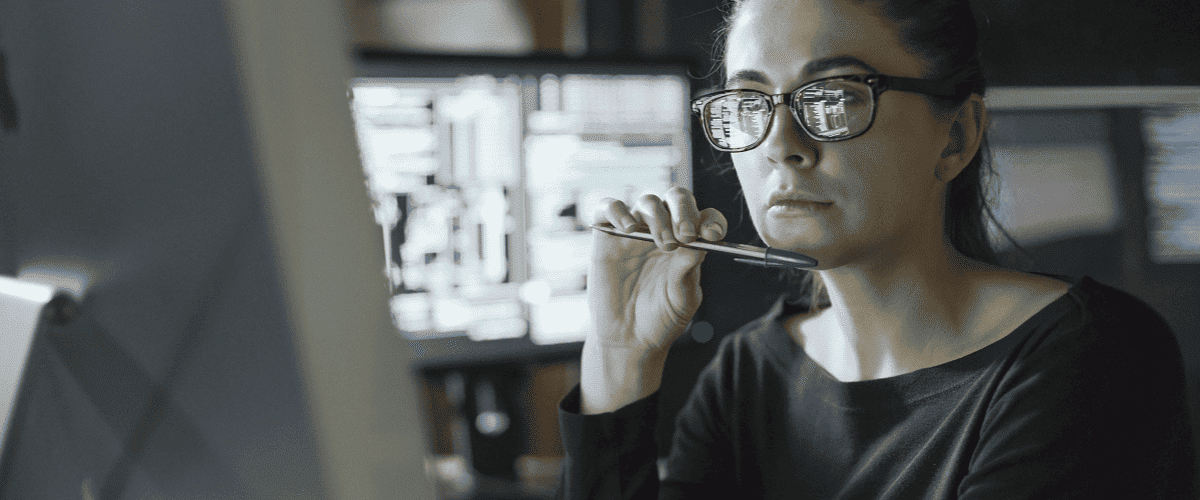
The healthcare industry heavily relies on medical software to provide patients with quality care and access to the latest treatments. However, healthcare professionals need knowledge and training to use these technologies.
This article explores the role of a clinical application specialist and the importance of their work. As the healthcare industry is all about keeping up with the latest technologies, it is equally important to know which specialists are helping to achieve this goal.
Clinical application specialists are those who play a vital role in onboarding and training healthcare professionals when it comes to working with new software solutions.
What is a clinical application specialist?
A clinical application specialist (CAS) is a professional responsible for training healthcare staff in the use of new software. They have sufficient expertise to provide training, support and assistance to medical personnel in the correct use of different systems and software.
In other words, they teach them on how to use new software and equipment. Medical imaging software or anaesthesia machines are just two examples.
Responsibilities & tasks
A clinical application specialist works with a variety of healthcare facilities and has the following duties and responsibilities:
- Choosing & implementing the right software for a healthcare organisation
- Assessing systems
- Documenting & testing software vendors
- Optimising software
- Troubleshooting & resolving problems
- Other activities related to transitioning to new equipment & software
- Training professionals in its use
Depending on the needs and requirements of the medical facility, a clinical application specialist provides the necessary tools for training medical staff who will use newly implemented software and systems.
They are responsible for providing technical support to medical professionals and ensuring that the technology is used correctly. Moreover, a clinical application specialist is responsible for building relationships with the healthcare industry to advance sales.
Their role is critical in helping healthcare professionals keep pace with the ever-changing technological landscape.
Education, training & necessary skills
In general, the level of education required to work as a clinical application specialist is a bachelor’s degree. Most employers expect applicants to have a degree in areas such as computer science, information science or medical information technology.
Many of those working as clinical application specialists have studied nursing or even business.
Therefore, the first step to working as a clinical applications specialist is to earn a bachelor’s degree. Subsequently, it is necessary to gain experience in a medical setting. Some employers require a minimum of two years previous experience in a medical facility.
The aim of this work is to understand more about the medical field, learn medical terminology and gain skills in clinical research and patient care.
In some cases, additional certifications and training may be required. Even after getting the job, a clinical application specialist must continue to learn and take advantage of training opportunities. Technology is advancing rapidly.
Thus, professionals need to keep up with the latest trends. They can do this by taking part in training courses and seminars on new products.
In terms of the skills required to become a clinical applications specialist, a person must possess several qualities:
- Technological expertise & technical skills: In order to work in this field, advanced skills in computer systems are required. Technical proficiency shows that they understand the medical equipment and software they will have to teach others to use. This will enable them to provide technical support and troubleshooting.
- Problem solving skills: Working with new software, systems and platforms, a CAS must be able to respond effectively to customer problems, to identify and analyse complex issues, determine the root cause and find solutions.
- Clinical knowledge: The reason for requiring experience in a healthcare setting is that a CAS must have a solid foundation in clinical practice and medical terminology. This is the only way to understand the needs of healthcare providers and patients.
- Strong communication skills: A CAS must be able to communicate effectively with software end users and be a good listener. Great communication skills will help to make themselves understood, even when they have to convey complex technical information. Learning new technologies can be a frustrating process, so a CAS must be patient and calm in such situations and demonstrate effective teaching skills.
- Flexibility & adaptability: A CAS must adapt to changes in technology and the healthcare environment. They need to continue their education and learn new skills, be able to work in a dynamic environment and be flexible. In some cases, they may be required to provide technical support at weekends or at night when medical software problems arise.
In summary, a clinical application specialist must demonstrate a mix of technical skills, communication skills, analytical thinking and adaptability.
Workplace & tasks
A clinical application specialist can work in a variety of settings: from hospitals and clinics to medical device companies and IT departments.
Depending on the environment, a typical working day may involve meeting with healthcare providers to understand their needs and providing training and technical support in the use of medical software.
They must also troubleshoot, install and regularly upgrade medical software and equipment in different medical facilities. At times, they may be required to conduct clinical research and product demonstrations.
The salary of a CAS depends on their experience and the country in which they work. For example, with 0 to 1 year of experience the salary range is $67,000 to $115,000 per year in the United States. These are the main things a person who intends to become a clinical application specialist should know.
Technology has become essential in healthcare, so CAS can be a promising career option.